Massively Parallel Remote Database Builds
If you have a fleet of databases to update, it could take a very long time to run your build on a single machine - even if you leverage the threaded model. To solve this problem, SQL Build Manager offers four ways to parallelize database builds across many compute resources: Azure Container Apps, Azure Batch, Kubernetes and Azure Container Instances (ACI).
In each method, compute resources area able to manage concurrency to help you maximize throughput while not overloading your SQL Servers. See Concurrency Options.
You can create a demo/sandbox environment to test and play with each method with Setting up an Azure Environment
Understanding remote build steps
Each remote build option follows the same basic steps to stage the required configuration and compute resources, then start and monitor the processing. Unless specified, these are sub-commands of each remote option: sbm k8s|containerapp|batch|aci
savesettings
Save a settings JSON file for the target compute environment. This step is optional, but is designed for reuse in subsequent commands and across multiple builds targeting the same environment. Each remote type has some variation of options, so use sbm {remote type} savesettings -h for specifics. You can also save sensitive information to Azure Key Vault by specifying a --keyvault value.
run
Single command used to execute by orchestrating the other commands decribed below.
Step-wide deployment
(note: the run command for orchestrates this for you)
prep
(named prestage for sbm batch) Creates the required Azure Blob storage container and uploads the package file and/or DACPAC so it is accessable to the compute resources. It will also configure any infrastructure templates and for Batch, will spin up the VMs in the node pool. The blob container is specfied by the --jobname parameter
enqueue
Remote executions pull their database targets from Azure Service Bus. This step creates a Service Bus Topic Subscription and uses the Override file as its list of targets, creating a message per target.
deploy
Deploys the compute infrastucture (for containerapp and aci) and automatically starts the build once the compute resources are available (containerapp, aci and batch). There is no equivalent step for Kubernetes, for this use the single k8s run command or manually run kubetcl commands to deploy the pods. Also no equivalent for sbm batch, this is handled by the batch run command.
monitor
By default the deploy command automatically flows into and starts monitoring. Monitoring polls the Service Bus Topic for remaining messages and Azure Event Hub for database processing events. A build is considered complete when the total number of database completion events (commits or errors) is equal to the total number of targets. No equivalent for sbm batch. Instead, Batch will direclty monitor the Batch job tasks for compeltion.
cleanup
An extra command for sbm batch. This will deprovision and remove VMs from the batch to ensure you aren’t billed for idle resources
Process Flow Details
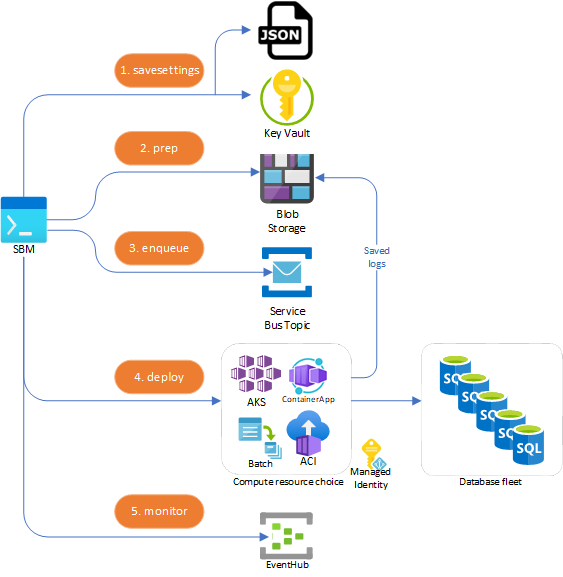
Start an Azure connection with the Azure CLI via az login. This will create an authentication token that the sbm tooling will use to connect to Key Vault and the other Azure services
savesettings- keys, connection strings and passwords saved in Azure Key Vault if--keyvaultspecified, otherwise it will be AES256 encrypted to the JSON file. Non-sensitive information is always saved in the json fileprep- The.sbmpackage and DACPAC (if provided) is uploaded to blob storage and resource specific templates are created and readied for deploymentenqueue- Using the--overridefile as a source, Service Bus Topic messages are enqueued, one for each target databasedeploy(run for batch) - The compute resources are created and immediately start processing messages from the Service Bus topic and performing the build on the targe databasesmonitor- the Service Bus Topic is monitored for remaining messages and EventHub for completion events. Once complets, the compute resource will upload the run logs to the blob storage container
If using a Managed Identity, the compute resources will leverage this identity vs. connection strings and passwords to access the various resources. See the Managed Identity documentation to see how each service is able to take advantage of this.